From Raman Frequency Combs to Supercontinuum Generation in Nitrogen-Filled Hollow-Core Anti-Resonant Fiber
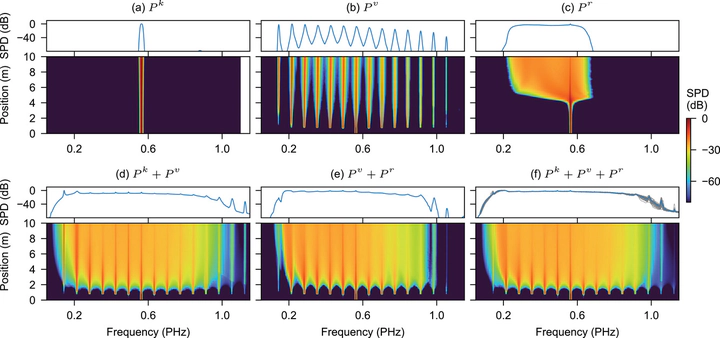 Numerical simulations of the spectral evolution. We model 20 ps duration, 532 nm wavelength, 80 μJ pump pulses in a 10 m long, 26 μm diameter hollow fiber filled with nitrogen with a pressure gradient from 1 to 40 bar. Each subplot includes the indicated contributions to the nonlinear polarization. SPD = relative spectral power density. These data are an ensemble average of 100 simulations to account for shot-to-shot fluctuations. To illustrate the shot-to-shot fluctuations the top panel of (f) shows each individual shot as a thin grey line, with the average in blue.
Numerical simulations of the spectral evolution. We model 20 ps duration, 532 nm wavelength, 80 μJ pump pulses in a 10 m long, 26 μm diameter hollow fiber filled with nitrogen with a pressure gradient from 1 to 40 bar. Each subplot includes the indicated contributions to the nonlinear polarization. SPD = relative spectral power density. These data are an ensemble average of 100 simulations to account for shot-to-shot fluctuations. To illustrate the shot-to-shot fluctuations the top panel of (f) shows each individual shot as a thin grey line, with the average in blue.
Abstract
A route to supercontinuum generation in gas-filled hollow-core anti-resonant fibers is demonstrated through the creation of a broad vibrational Raman frequency comb followed by continuous broadening and merging of the comb lines through either rotational Raman scattering or the optical Kerr effect. The demonstration experiments, utilizing a single pump pulse with 20 ps duration at 532 nm in a nitrogen-filled fiber, produce a supercontinuum spanning from 440 to 1200 nm, with an additional deep ultraviolet continuum from 250 to 360 nm. Numerical results suggest that this approach can produce even broader supercontinuum spectra extending from the ultraviolet to mid-infrared.
Type
Publication
Laser & Photonics Reviews 16 2100426 (2022)